YouTube
David Seaman is the #Pizzagate King of the Internet.
On Twitter, Seaman posts dozens of messages a day to his 66,000 followers, often about the secret cabal — including Rothschilds, Satanists, and the other nabobs of the New World Order — behind the nation’s best-known, super-duper-secret child sex ring under a DC pizza parlor.
But it’s on YouTube where he really goes to work. Since Nov. 4, four days before the election, Seaman has uploaded 136 videos, more than one a day. Of those, at least 42 are about Pizzagate. The videos, which tend to run about eight to fifteen minutes, typically consist of Seaman, a young, brown-haired man with glasses and a short beard, speaking directly into a camera in front of a white wall. He doesn’t equivocate: Recent videos are titled “Pizzagate Will Dominate 2017, Because It Is Real” and “PizzaGate New Info 12/6/16: Link To Pagan God of Pedophilia/Rape.”
Seaman has more than 150,000 subscribers. His videos, usually preceded by preroll ads for major brands like Quaker Oats and Uber, have been watched almost 18 million times, which is roughly the number of people who tuned in to last year’s season finale of NCIS, the most popular show on television.
His biography reads, in part, “I report the truth.”
In the aftermath of the 2016 presidential election, the major social platforms, most notably Twitter, Facebook, and Reddit, have been forced to undergo painful, often public reckonings with the role they play in spreading bad information. How do services that have become windows onto the world for hundreds of millions of people square their desire to grow with the damage that viral false information, “alternative facts,” and filter bubbles do to a democracy?
And yet there is a mammoth social platform, a cornerstone of the modern internet with more than a billion active users every month, which hosts and even pays for a fathomless stock of bad information, including viral fake news, conspiracy theories, and hate speech of every kind — and it’s been held up to virtually no scrutiny: YouTube.
The entire contemporary conspiracy-industrial complex of internet investigation and social media promulgation, which has become a defining feature of media and politics in the Trump era, would be a very small fraction of itself without YouTube. Yes, the site most people associate with “Gangnam Style,” pirated music, and compilations of dachshunds sneezing is also the central content engine of the unruliest segments of the ascendant right-wing internet, and sometimes its enabler.
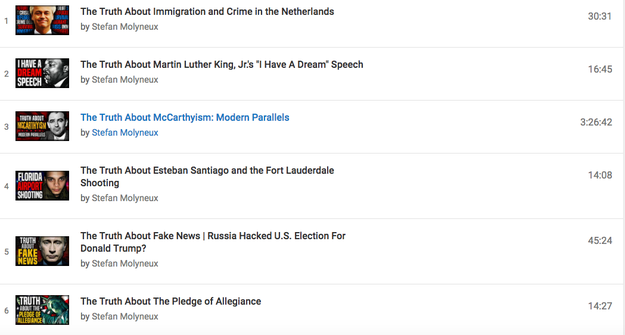
To wit, the conspiracy-news internet’s biggest stars, some of whom now enjoy New Yorker profiles and presidential influence, largely live on YouTube. Infowars — whose founder and host, Alex Jones, claims Sandy Hook didn’t happen, Michelle Obama is a man, and 9/11 was an inside job — broadcasts to 2 million subscribers on YouTube. So does Michael “Gorilla Mindset” Cernovich. So too do a whole genre of lesser-known but still wildly popular YouTubers, people like Seaman and Stefan Molyneux (an Irishman closely associated with the popular “Truth About” format). As do a related breed of prolific political-correctness watchdogs like Paul Joseph Watson and Sargon of Akkad (real name: Carl Benjamin), whose videos focus on the supposed hypocrisies of modern liberal culture and the ways they leave Western democracy open to a hostile Islamic takeover. As do a related group of conspiratorial white-identity vloggers like Red Ice TV, which regularly hosts neo-Nazis in its videos.
“The internet provides people with access to more points of view than ever before,” YouTube wrote in a statement. “We're always taking feedback so we can continue to improve and present as many perspectives at a given moment in time as possible.”
YouTube
All this is a far cry from the platform’s halcyon days of 2006 and George Allen’s infamous “Macaca” gaffe. Back then, it felt reasonable to hope the site would change politics by bypassing a rose-tinted broadcast media filter to hold politicians accountable. As recently as 2012, Mother Jones posted to YouTube hidden footage of Mitt Romney discussing the “47%” of the electorate who would never vote for him, a video that may have swung the election. But by the time the 2016 campaign hit its stride, and a series of widely broadcast, ugly comments by then-candidate Trump didn’t keep him out of office, YouTube’s relationship to politics had changed.
Today, it fills the enormous trough of right-leaning conspiracy and revisionist historical content into which the vast, ravening right-wing social internet lowers its jaws to drink. Shared widely everywhere from white supremacist message boards to chans to Facebook groups, these videos constitute a kind of crowdsourced, predigested ideological education, offering the “Truth” about everything from Michelle Obama’s real biological sex (760,000 views!![]() to why medieval Islamic civilization wasn’t actually advanced.
to why medieval Islamic civilization wasn’t actually advanced.
Frequently, the videos consist of little more than screenshots of a Reddit “investigation” laid out chronologically, set to ominous music. Other times, they’re very simple, featuring a man in a sparse room speaking directly into his webcam, or a very fast monotone narration over a series of photographs with effects straight out of iMovie. There’s a financial incentive for vloggers to make as many videos as cheaply they can; the more videos you make, the more likely one is to go viral. David Seaman’s videos typically garner more than 50,000 views and often exceed 100,000. Many of Seaman’s videos adjoin ads for major brands. A preroll ad for Asana, the productivity software, precedes a video entitled “WIKILEAKS: Illuminati Rothschild Influence & Simulation Theory”; before “Pizzagate: Do We Know the Full Scope Yet?&033;” it’s an ad for Uber, and before “HILLARY CLINTON&039;S HORROR SHOW,” one for a new Fox comedy. (Most YouTubers have no direct control over which brands&039; ads run next to their videos, and vice versa.)
This trough isn’t just wide, it’s deep. A YouTube search for the term “The Truth About the Holocaust” returns half a million results. The top 10 are all Holocaust-denying or Holocaust-skeptical. (Sample titles: “The Greatest Lie Ever Told,” which has 500,000 views; “The Great Jewish Lie”; “The Sick Lies of a Holocaust™ &039;Survivor.&039;”) Say the half million videos average about 10 minutes. That works out to 5 million minutes, or about 10 years, of “Truth About the Holocaust.”
Meanwhile, “The Truth About Pizzagate” returns a quarter of a million results, including “PizzaGate Definitive Factcheck: Oh My God” (620,000 views and counting) and “The Men Who Knew Too Much About PizzaGate” (who, per a teaser image, include retired Gen. Michael Flynn and Andrew Breitbart).
Sometimes, these videos go hugely viral. “With Open Gates: The Forced Collective Suicide of European Nations” — an alarming 20-minute video about Muslim immigration to Europe featuring deceptive editing and debunked footage — received some 4 million views in late 2015 before being taken down by YouTube over a copyright claim. (Infowars: “YouTube Scrambles to Censor Viral Video Exposing Migrant Invasion.”) That’s roughly as many people as watched the Game of Thrones Season 3 premiere. It’s since been scrubbed of the copyrighted music and reuploaded dozens of times.
First circulated by white supremacist blogs and chans, “With Gates Wide Open” gained social steam until it was picked up by Breitbart, at which point it exploded, blazing the viral trail by which conspiracy-right “Truth” videos now travel. Last week, President Trump incensed the nation of Sweden by falsely implying that it had recently suffered a terrorist attack. Later, he clarified in a tweet that he was referring to a Fox News segment. That segment featured footage from a viral YouTube documentary, Stockholm Syndrome, about the dangers of Muslim immigration into Europe. Sources featured in the documentary have since accused its director, Ami Horowitz, of “bad journalism” for taking their answers out of context.
So what responsibility, if any, does YouTube bear for the universe of often conspiratorial, sometimes bigoted, frequently incorrect information that it pays its creators to host, and that is now being filtered up to the most powerful person in the world? Legally, per the Digital Millennium Copyright Act, which absolves service providers of liability for content they host, none. But morally and ethically, shouldn’t YouTube be asking itself the same hard questions as Facebook and Twitter about the role it plays in a representative democracy? How do those questions change because YouTube is literally paying people to upload bad information?
And practically, if YouTube decided to crack down, could it really do anything?
YouTube does “demonitize” videos that it deems “not advertiser-friendly,” and last week, following a report in the Wall Street Journal that Disney had nixed a sponsorship deal with the YouTube superstar PewDiePie over anti-Semitic content in his videos, YouTube pulled his channel from its premium ad network. But such steps have tended to follow public pressure and have only affected extremely famous YouTubers. And it’s not like PewDiePie will go hungry; he can still run ads on his videos, which regularly do millions of views.
Ultimately, the platform may be so huge as to be ungovernable: Users upload 400 hours of video to YouTube every minute. One possibility is drawing a firmer line between content the company officially designates as news and everything else; YouTube has a dedicated News vertical that pulls in videos from publishers approved by Google News.
Even there, though, YouTube has its work cut out for it. On a recent evening, the first result I saw under the “Live Now – News” subsection of youtube.com/news was the Infowars “Defense of Liberty 13 Hour Special Broadcast.” Alex Jones was staring into the camera.
Quelle: <a href="How YouTube Serves As The Content Engine Of The Internet&039;s Dark Side“>BuzzFeed

Published by